
Here, for example, the single difference in the sequences can be eliminated (red for blue or vice versa). Repairs can then be made (probably by the mechanism of homologous recombination). All that is needed is to form a loop so that the two sequences line up side-by-side. This orientation and redundancy may help ensure that a deleterious mutation in one copy of the set can be repaired using the information in another copy of that set. (The dashes represent the thousands of base pairs that separate adjacent palindromes.) The human Y chromosome contains 7 sets of genes - each set containing from 2 to 6 nearly-identical genes - oriented back-to-back or head-to-head that is, they are inverted repeats like the portion shown here.

Reverse the order of the reverse complement ( CTA) and add it to the end of the forward strand - TAGCTA.Calculate the reverse complement of the sequence - ATC.
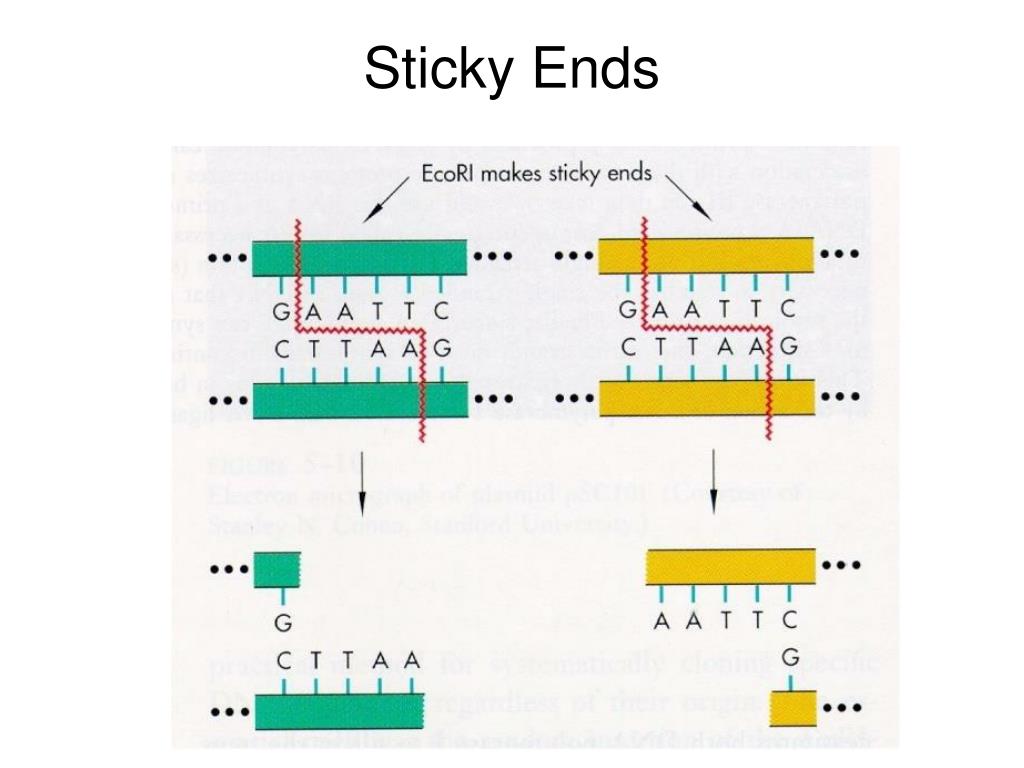
Starting with the original sequence - TAG.TAGCTA) can be reconstructed from just knowing the first three bases on one strand: For example, a six-base recognition sequence (e.g. This pattern makes it possible to reconstruct a palindromic sequence from one-half of one strand. The complement to the whole six base strand is CCTAGG, read backwards (as it would be when reading from 5’ to 3’ on the complementary strand) is GGATCC, an exact match for the original strand. Note the first three bases GGA are followed by the complement of those three bases in reverse order: TCC. For example the recognition sequence for BamHI is GGATCC. Palindromic sequences are a short run of bases (typically 3 to 5 in length), follow by their complementary bases in reverse order. As the palindromic sequence is recognised by the enzyme regardless of which side it approaches the DNA, hence a palindromic sequence enhances the likelihood of. They are probably more properly referred to as palindromic sequences to distinguish them from language palindromes. In English, the term palindrome refers to a string of letters that have the same meaning written in both directions some classic English palindrome are kayak, civic, noon, and racecar.Īs a set of paired sequences (one on each of the strands of a double strand of DNA), the palindromes recognized by restriction enzymes follow a slightly different set of rules.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
